Hubei's eco resources help to build industries


Hubei province, a key part of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, is developing industries by leveraging its ecological resources along the river.
In early winter, the clear waters of the Danjiangkou Reservoir in Shiyan city reflect the busy activity of a beverage industrial park. The reservoir, the core water source area for the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, has transferred more than 69 billion cubic meters of water to the north over the past decade, nourishing 26 large and medium-sized cities and about 100 million people along the route.
Shiyan has built a high-level beverage industry under the "Wudang Mountain Water" brand, attracting 72 well-known companies, including Nongfu Spring, Jinmailang and PepsiCo. The city has created a complete industrial chain covering drinking water, tea drinks, fruit juices and beer, cultivating a beverage cluster with a total output value exceeding 100 billion yuan ($14.32 billion).
Inside the Beijing Yiqing Food (Danjiangkou) Industrial Park in Shiyan, bottles of Beibingyang soda drink roll off a fully automated production line at high speed.
"The soda drink is a bit different. It carries the clear water of Danjiangkou and the sweetness of Wudang honey oranges," said Li Qiang, quality inspector at Beijing Yiqing.
The company purchases about 150,000 metric tons of local oranges annually, accounting for 40 percent of the local total production, directly increasing the income of 28,000 orange farmers.
To protect the reservoir's clean water, water companies in Danjiangkou allocate a certain percentage of profits annually to an ecological compensation fund.
Beijing Yiqing is equipped with a sewage treatment station and a green energy system. Waste residue from the juice workshop is processed into organic fertilizer, and some production processes use a photovoltaic model, forming a virtuous cycle of water source protection, product development, and market sales, the company said.
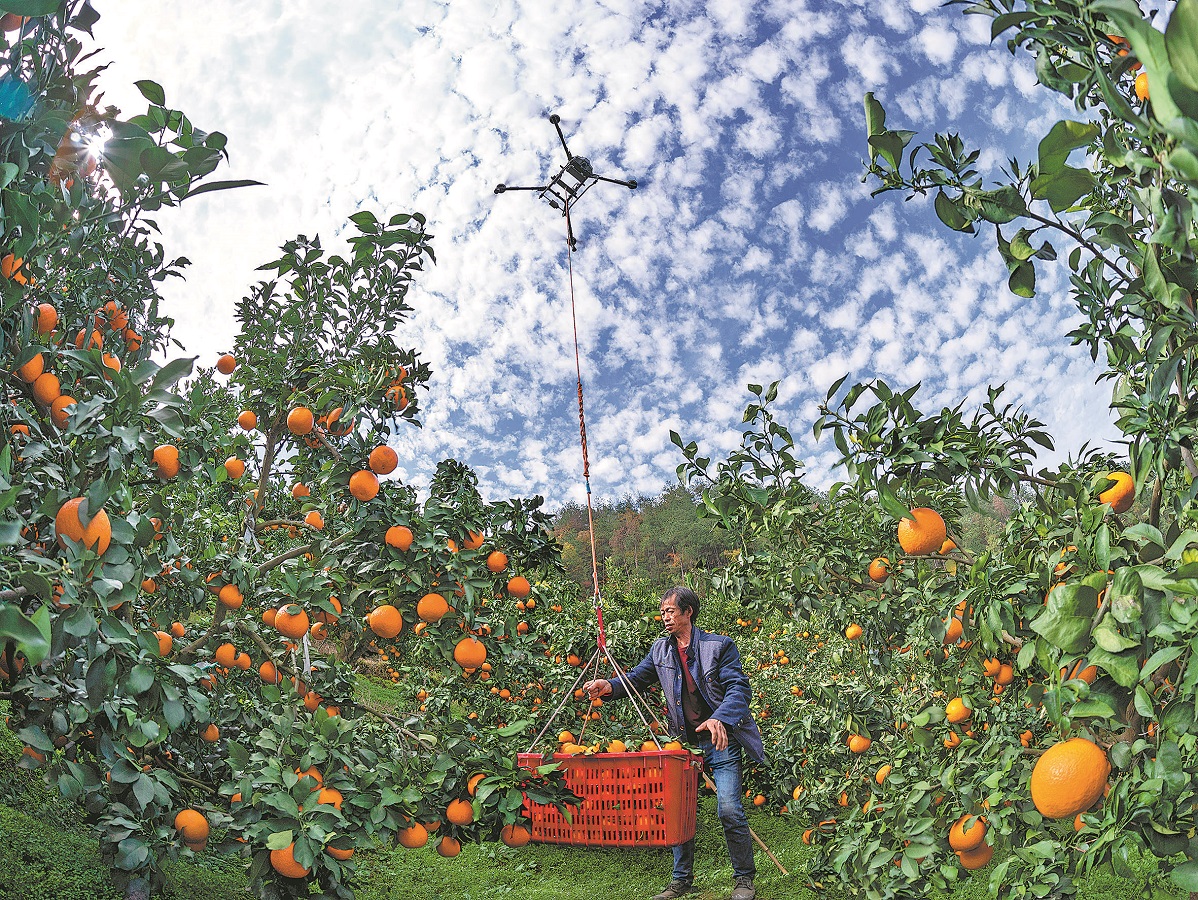
Downstream along the Yangtze River, the expansive orange groves of Zigui county in the Three Gorges Reservoir area offer another example of the "two mountains" concept that "lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets".
In the orange orchard in Wangjialing village, golden oranges hang from the branches. Farmer Guo Xingcheng lightly manipulates a remote control, and a drone carrying a 60-kilogram basket of oranges takes off, flies over a 100-meter-high ridge in one minute, and lands steadily next to a transport vehicle.
Guo returned to his hometown in 2011 after doing odd jobs outside and took over the 2-hectare orange orchard from his parents.
"In the past, picking oranges relied on shoulder carrying and manual spraying for pest control, keeping us busy all the time," he said. "The high-intensity labor caused me significant stress."
In the summer of 2020, the efficiency of pesticide drones inspired Guo to purchase equipment and diligently study operational techniques, eventually obtaining a Civil Aviation Administration of China drone license. In 2022, he successfully developed drone-based orange lifting techniques, reducing a half-hour manual task to just one minute.
He also registered a company, formed a service team of 40 members, and equipped it with 17 agricultural drones and five transport vehicles.
The transformation of Wangjialing reflects the broader upgrade of Zigui's orange industry. In the intelligent sorting center, machines can sort oranges by size, moisture, and sugar content with a single click. A cold chain logistics system spanning urban and rural areas extends the shelf life of fresh oranges to several months. The "Zigui Navel Orange" national geographical indication brand is gaining recognition.
The county's orange planting area now totals 26,667 hectares, with an output of 1 million tons and a comprehensive output value of nearly 20 billion yuan. More than 70 percent of residents are engaged in orange-related industries, supporting stable income growth for 260,000 people. Groups of new farmers, including drone operators and e-commerce anchors, continue to grow, becoming the backbone of industrial revitalization.
Elsewhere, Shennongjia has explored quantifiable and tradeable ways to realize the value of ecological resources. With 91.1 percent forest coverage and an annual carbon absorption capacity of 1.0968 million tons, the region has pioneered carbon finance innovations. It has introduced models such as carbon sink loans and ecological loans, using carbon sink resources as collateral to provide credit support to ecological enterprises.
By August 2024, Shennongjia had issued nearly 120 million yuan in carbon sink loans, including 18.4 million yuan in carbon forest loans to two enterprises, using afforestation carbon sink income as a repayment source.
Additionally, the local forestry management bureau partnered with State Grid New Energy Cloud Technology to promote the listing of forestry carbon sink resources, effectively turning ecological resources into assets and capital.
From Danjiangkou's water economy and Zigui's orange industry to Shennongjia's carbon sink loans, Hubei has focused on building a system for realizing the value of ecological products, establishing a comprehensive and multilayered framework for converting ecological value.
In 2024, the total value of Hubei's ecological products exceeded 1.2 trillion yuan, with the added value of green industries accounting for 25.6 percent of GDP.